Quality products and a resilient business are vital in competitive fields like pharmaceuticals. Here’s where quality assurance (QA) comes in. It lays the groundwork for smooth operations and happy users. But the fast-paced tech world demands more. Enter risk management – the proactive partner that identifies issues before they cause problems.
This blog dives into the powerful connection between QA and risk management. We’ll see why a strong risk management process in QA is key. Then, we’ll explore how risk-aware QA professionals safeguard quality and business.
What is Quality Assurance?
Ever wonder how companies guarantee quality? It’s all thanks to quality assurance, the behind-the-scenes hero. QA is a systematic process that ensures everything meets top standards.
QA doesn’t just catch mistakes; it prevents them. Imagine having a quality inspector on the lookout throughout the software development process. Happy customers, consistent performance, and meeting regulations – that’s the brilliance of quality assurance.
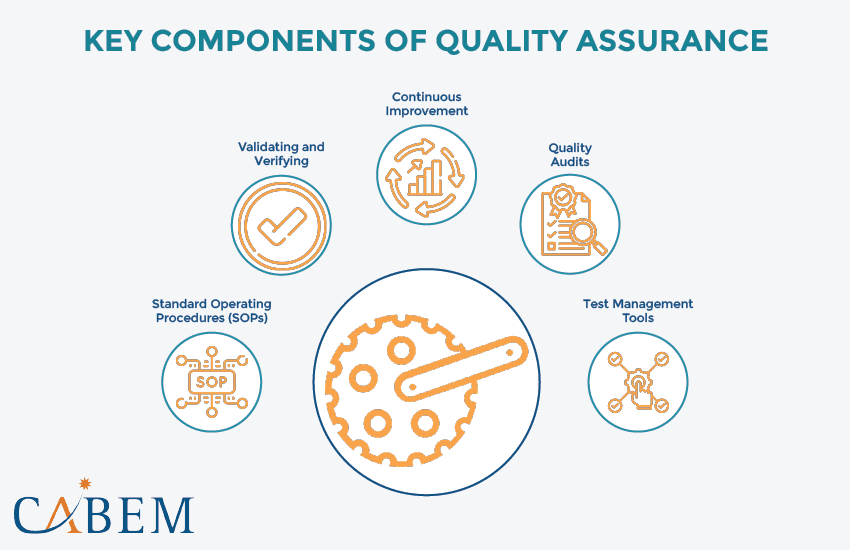
Key Components of Quality Assurance
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
SOPs exist at every level and in every field to ensure the uniformity and quality of any product or service. They also help comb out any human errors or issues one might naturally overlook when working.- Importance: SOPs help businesses keep discipline and compliance with legal regulations.
- Implementation: Businesses update SOPs as per the changes in technology, legislation, and recommendations.
- Validating and Verifying
Imagine a quality inspector with two tools:- Validation: This ensures that processes and systems perform as intended. Validation also determines if the results meet predetermined specifications. Types of validation include process validation, method validation, and cleaning validation.
- Verification: This involves checking and testing to confirm that products meet quality standards. Together, they guarantee a smooth-running quality machine.
- Continuous Improvement
QA is a journey, not a destination. Regularly reflecting on and optimizing the process is key. This is where methodologies like Six Sigma and Lean come in handy. They help streamline procedures and maximize positive outcomes in QA. - Quality Audits
Think of audits as internal and external quality checkups. Internal audits ensure the organization follows its own standards. External audits verify compliance with external regulations. Both are crucial for maintaining a healthy and robust QA system. - Test Management Tools
Using software designed for managing tests can help improve efficiency. These tools streamline tasks like:- Managing test cases
- Tracking defects
- Automating repetitive actions
- Generating reports
What is Risk Management?
Risk management is a cornerstone of organizational resilience. This systematic process helps identify, assess, and control threats to an organization’s objectives. These threats, or risks, can come from various sources, including:
- Financial uncertainties like market fluctuations or unexpected expenses.
- Legal liabilities arising from regulatory changes or lawsuits.
- Technology disruptions due to cyber threats or outdated infrastructure.
- Strategic management errors such as missed market opportunities or flawed product launches.
- Unforeseen events like natural disasters or accidents.
An efficient risk management system from CABEM helps organizations assess the risk landscape. First, the tool identifies individual risks. Then, it analyzes their potential cascading effects on achieving strategic objectives.
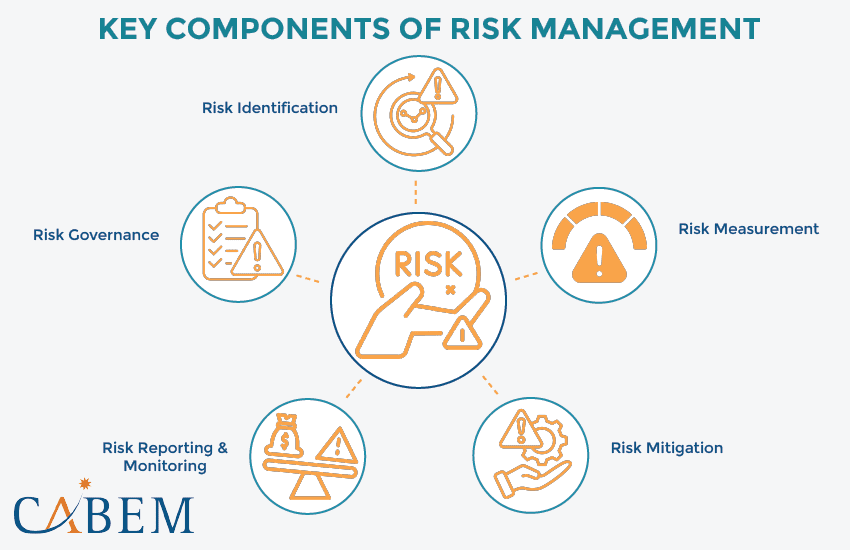
Key Components of Risk Management
- Risk Identification
- Defining the Risk: This involves creating a list of threats an organization may face. Threats include financial, legal, operational, strategic, and technological risks.
- Prioritization: There are two risk categories: “core” and “non-core.” Businesses categorize risks based on their impact on achieving strategic goals and growth. Core risks are essential for business success. Non-core risks are minimal or controllable.
- Risk Measurement
- Quantifying Risks: This step assesses the risk’s financial impact and likelihood of occurrence.
- Challenges: Measuring specific risks can vary in difficulty. Some, like market risks, have observable data (e.g., market prices) for assessment. Others, like operational risk, require a blend of data and expert judgment.
- Risk Measures: One can measure specific risks by their potential impact on profit and loss (P/L). Businesses should also consider volatility (how much the P/L can fluctuate). Aggregate risk measures like Value at Risk (VaR) offer a broader view of potential losses.
- Risk Mitigation
Organizations can develop mitigation strategies by identifying and measuring risks. This might involve selling assets/liabilities, acquiring insurance, hedging with derivatives, or diversification. - Risk Reporting & Monitoring
Regular reporting on both individual and aggregate risk measures is crucial. This helps ensure risks stay within acceptable levels. The reporting frequency varies by industry. It can be daily for financial institutions and less frequent for others. Reports should reach authorized personnel to adjust risk exposures based on changing circumstances. - Risk Governance
This ensures all employees perform their duties as per the risk management framework. Risk governance involves- Defining roles
- Segregating duties (preventing conflicts of interest)
- Assigning authority for approving core risks
- Setting risk limits
- Providing general oversight
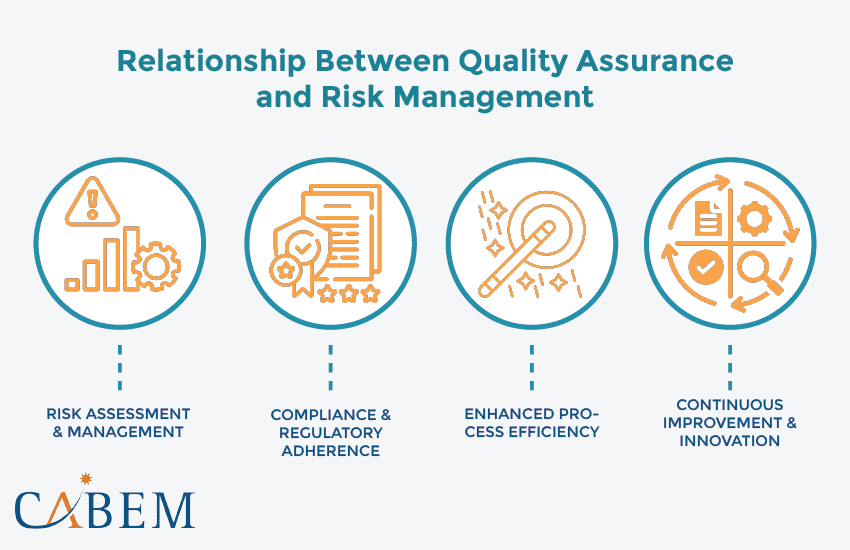
Relationship Between Quality Assurance & Risk Management
For industries like pharmaceuticals, a single mistake can have dire consequences. Here, quality assurance and risk assessment become inseparable partners. They help businesses protect both product safety and efficacy.
QA and risk management systems combine to create a solid framework. This partnership helps improve product quality and the stability of the organization. Let’s have a look at how these two disciplines work hand-in-hand:
Risk Assessment & Management
QA Perspective: QA catches quality issues early. For example, it can spot impurities in pharmaceutical raw materials. This helps minimize contamination risks.
Risk Management Perspective: Risk management assesses these risks and plans for disruptions. Examples include analyzing supply chain disruptions and finding backup suppliers. This ensures smoother operations.
Compliance & Regulatory Adherence
QA: QA safeguards the organization from regulatory penalties by ensuring adherence to product-related legislation (GMP, GLP, etc.). This proactive approach minimizes the risk of non-compliance and associated fines.
Risk Management: Risk management monitors changes in laws and regulations. It assesses potential impacts on business operations and compliance procedures. This foresight allows for timely adjustments to business continuity plans and compliance strategies.
Enhanced Process Efficiency
QA: QA develops procedures for managing production variability, which improves efficiency and productivity. This includes using improvement methodologies focused on cost reduction and streamlined business operations.
Risk Management: Risk reduction identifies potential operational risks that could impact these processes. Recognizing risks helps implement preventive measures that ensure business continuity and smooth operation.
Continuous Improvement & Innovation
QA: Regularly updates the quality standards to the modern tendencies of the industry. This entails embracing new technologies and techniques for enhanced product quality.
Risk Management: Tracks emerging risks and trends. Ensures improvement activities address both future risks and opportunities. Uses risk and opportunity mapping to stay ahead of the curve.
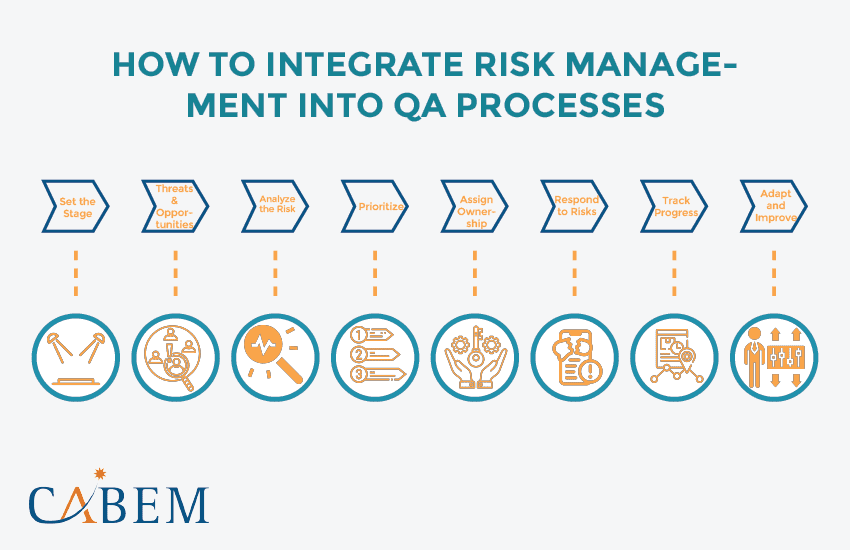
How to Integrate Risk Management into QA Processes
Effectively integrating risk assessment and management into QA processes requires a step-by-step approach. Here’s a breakdown of key stages:
- Set the Stage: Consider the ever-changing business landscape (VUCA). Analyze internal/external contexts using PESTLE or SWOT. Identify stakeholders and vulnerable objectives.
- Threats & Opportunities: Evaluate risk exposure – how threats or opportunities might impact objectives. Brainstorm with colleagues for a wider view.
- Analyze the Risk: Research the risk’s impact on schedule and budget.
- Prioritize: Not all risks are equal. Categorize them (high, medium, low) for targeted response plans.
- Assign Ownership: Each risk needs an owner – someone to track and take action if it happens.
- Respond to Risks: Are these opportunities or threats? Execute the response plan (leverage or mitigate).
- Track Progress: The risk owner monitors the response strategy’s effectiveness.
- Adapt and Improve: Regularly review the risk management strategy. Use the insights to improve future responses.
Examples of Risk Management and Quality Assurance Across Industries
Every industry operates like a unique ecosystem. They face different challenges, regulations, and market forces. The core principles of QA and risk management remain the same. But, their implementation may differ. Let’s dive into a few key industries and their signature risk management styles:
Software Development: Building Bulletproof Software
In software development, risk reduction is the key to delivering reliable products. QA teams use risk management systems to identify potential vulnerabilities early. This helps to ensure a smooth user experience and reduce crashes. Imagine a software company that identifies performance bottlenecks early on. The proactive approach leads to robust, reliable software.
Manufacturing Industry: Safeguarding Quality
The risk management process is vital for manufacturers. It helps maintain strict quality standards and regulations. QA teams use mitigation strategies to pre-empt issues like production defects. By proactively addressing these threats, organizations stay ahead of the curve. This process helps ensure top-notch product quality, optimize production, and maintain customer trust.
Healthcare Sector: Prioritizing Patient Safety
Patient safety and regulatory compliance are paramount in healthcare. QA teams often leverage risk management frameworks. They assess clinical processes, medical device safety, and data security risks. This ensures safe, effective treatments and adherence to regulations. Implementing an effective risk management process helps:
- Protects patients
- Fosters compliance
- Reinforces organizational credibility
Advanced Tools and Technologies
Quality Risk Management (QRM)
Quality Risk Management forms the backbone of any pharmaceutical quality system. This systematic process assesses controls, communicates, and reviews risks to product quality. It fosters a deep understanding of processes and identifies quality risks.
ICH Q9 Guidelines
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) Q9 provides a framework for QRM. It emphasizes a risk-based approach to quality management. This ensures that the effort, formality, and documentation align with the risk level.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Software
ERM software integrates risk management activities across the organization. It provides a centralized platform for risk identification, assessment, and mitigation. It enables real-time risk monitoring and reporting, facilitating better decision-making.
Data Analytics and AI
Advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are enhancing QA and Risk Management. These technologies enable predictive analytics. This allows businesses to identify potential risks before they materialize.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts
Blockchain and smart contracts represent two of the most groundbreaking software technologies. They enable decentralization, transparency, and trust. They eliminate intermediaries and reduce the risk of fraud.
Conclusion
QA and risk management form a powerful duo. This partnership is essential, especially in pharmaceuticals, where quality is paramount.
Together, they build a strong framework. This safeguards quality, optimizes processes, and strengthens resilience. This translates to:
- Enhanced Product Quality
- Improved Regulatory Compliance
- Streamlined Operations
- Continuous Innovation
By integrating risk management into QA, businesses navigate the ever-changing landscape with confidence. This ensures high-quality products, fosters trust, and positions companies for growth.
Looking to supercharge your QA efforts with a seamless risk management solution? CABEM’s Risk Manager empowers your QA team by simplifying the vendor evaluation process. Experience the power of a unified QA and risk management approach with CABEM!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is a software quality assurance certification worth getting?
Absolutely! QA certifications validate skills, show commitment to QA, and ensure knowledge of best practices. This means faster onboarding, quicker integration, and, ultimately, a higher-quality product. Certified professionals often prove to be an asset to their employers, delivering exceptional results.
What is the best way to maintain a quality assurance certification?
Maintaining your QA certifications is crucial, but it can be a juggling act. CABEM’s Competency Management System simplifies the process. You can track renewal dates, identify skill gaps, and enforce knowledge sharing. This ensures your team stays current with industry trends and best practices. By keeping your certifications active and your team sharp, CABEM empowers you to aim for consistent quality.
Should you use QA dashboards on your project?
Of course, using QA dashboards is a wise decision. These dashboards not only help teams stay in sync with one another, but they are also advantageous for clients who require regular progress reports.

